Timing Strategies for Invasive Plant Control
Effective invasive plant management depends heavily on timing. Proper scheduling ensures the best results in controlling and eradicating invasive species, minimizing environmental impact, and reducing long-term costs.
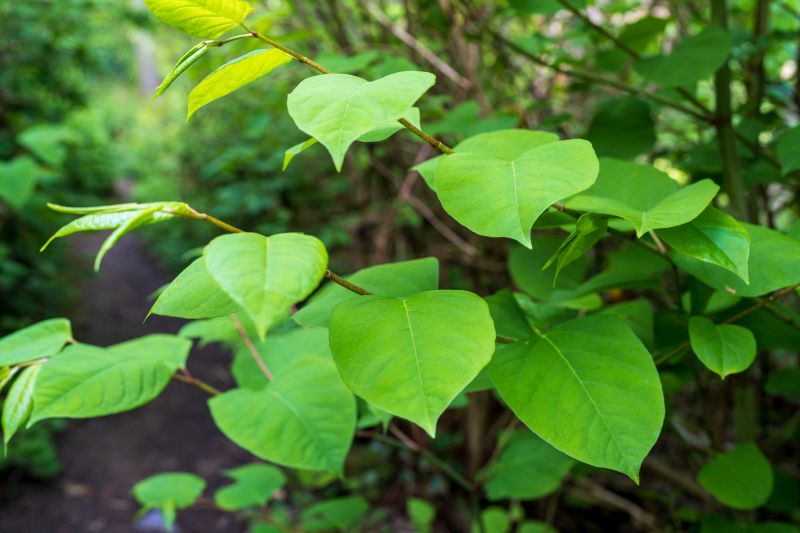

Spring is ideal for invasive plant control as many species are actively growing, making treatments more effective.
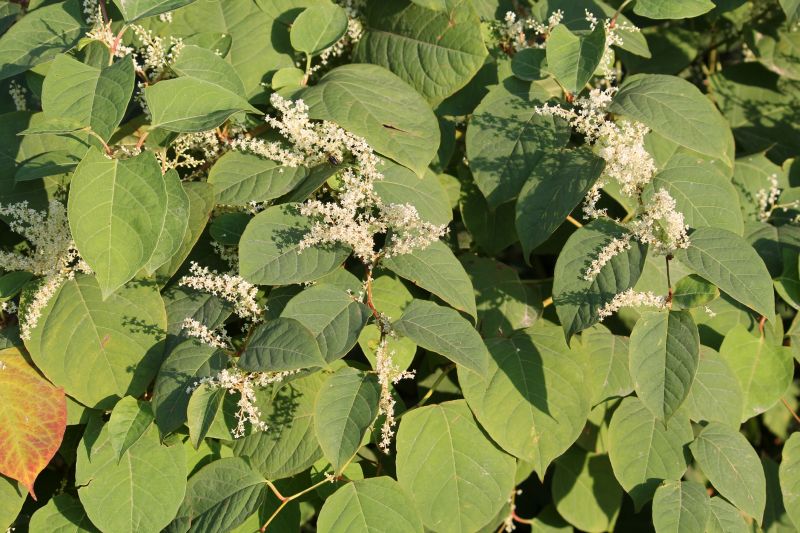

Summer management targets mature invasive plants, especially during flowering and seed production stages.

Fall offers opportunities to treat plants before seed dispersal, preventing further spread.

Ways to make Invasive Plant Managements work in tight or awkward layouts.

Popular materials for Invasive Plant Managements and why they hold up over time.

Simple add-ons that improve Invasive Plant Managements without blowing the budget.

High-end options that actually feel worth it for Invasive Plant Managements.

Finishes and colors that play nicely with Invasive Plant Managements.
Invasive plant management involves identifying, controlling, and removing non-native species that threaten native ecosystems. Timing is crucial because many invasive species have specific periods of growth, seed production, and dormancy. Implementing control measures at optimal times can significantly reduce the spread and impact of invasive plants.
Understanding the life cycles of invasive species helps determine the best management times for maximum effectiveness.
Proper timing of interventions can decrease invasive populations by up to 70%, reducing long-term management costs.
Regular monitoring during different seasons allows for timely interventions and better resource allocation.
Targeting invasive plants before seed dispersal is essential to prevent new infestations.
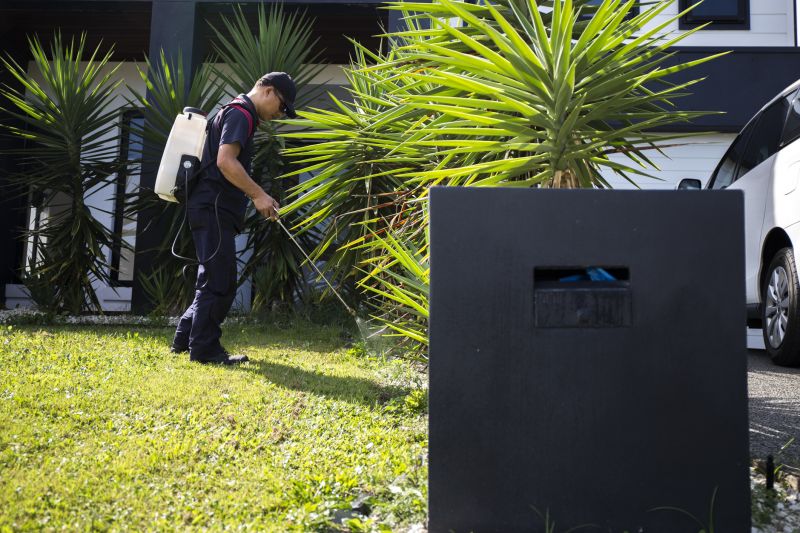

Spring treatments focus on young, actively growing invasive plants for better control.
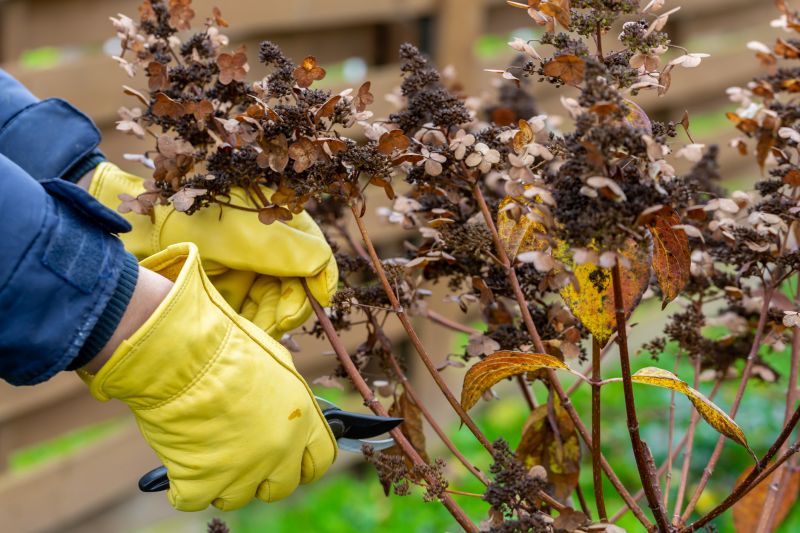

Summer is suitable for targeting mature invasive plants during flowering.
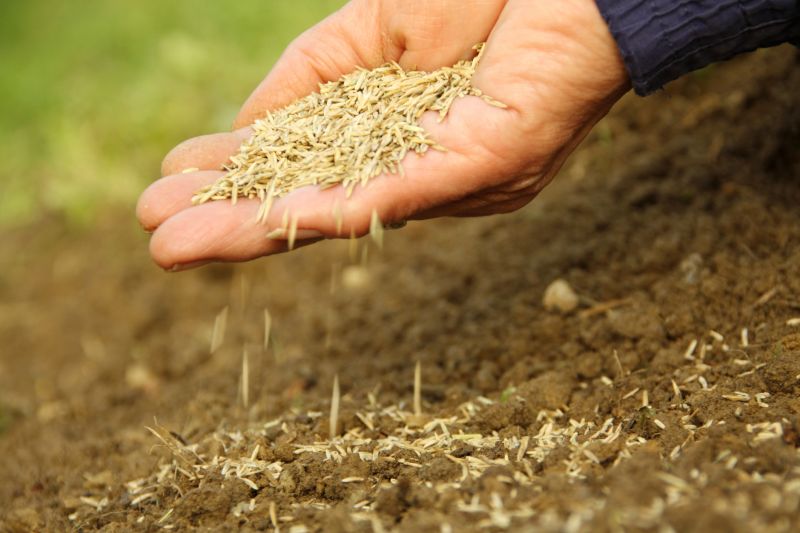

Fall management aims to reduce seed production and prevent further spread.

Ongoing assessment ensures invasive species are effectively managed across seasons.

Little measurements that prevent headaches on Invasive Plant Managements day.

A 60-second routine that keeps Invasive Plant Managements looking new.
| Season | Recommended Activities |
|---|---|
| Spring | Identify and treat young invasive plants; monitor growth. |
| Summer | Target mature plants during flowering; apply control methods. |
| Fall | Treat plants before seed dispersal; prepare for winter dormancy. |
| Winter | Conduct surveys and planning for upcoming seasons. |
| Early Spring | Begin early detection and rapid response. |
| Late Summer | Assess effectiveness of treatments and plan follow-up. |
Invasive plant management requires strategic timing aligned with the species' growth patterns. Proper scheduling enhances control success and reduces the likelihood of invasive species establishing new populations. Regular monitoring and adaptive management are key components of an effective invasive plant control program.

Removing invasive plants during peak growth maximizes control effectiveness.

Targeting invasive plants before seed release prevents future infestations.

Planning treatments according to seasonal growth cycles optimizes resource use.

Follow-up assessments ensure invasive species do not resurge.

A frequent mistake in Invasive Plant Managements and how to dodge it.
Small tweaks to make Invasive Plant Managements safer and easier to use.

Lower-waste or water-saving choices for Invasive Plant Managements.

The short, realistic tool list for quality Invasive Plant Managements.
Interested in managing invasive plants effectively? Filling out the contact form can provide tailored information and guidance on optimal timing and treatment strategies for invasive plant control efforts.
